A
Ackermann Steering: a simple mechanism to approximate ideal steering where each wheel is given its own pivot. Ackermann steering solves most of the problems of turntable steering: the space required by each wheel is significantly reduced and the moment arm transmitting back imperfections in the road if reduced.

Adiabatic Humidification: is the process when finely atomized water is introduced into the air. Adiabatic humidification injects water (not steam) directly into the air using a spray mechanism or wetted medium, and the heat from the surrounding air causes the water to evaporate. Adiabatic Humidifiers are the ideal humidity solution when Steam or Gas are not available, they are also energy efficient and give precise Humidity Control.
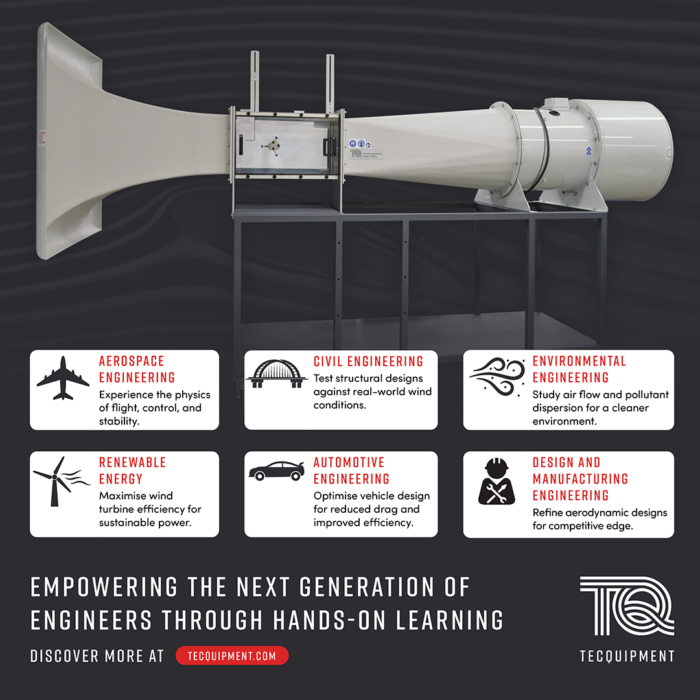
Aerofoil: A curved surface structure designed to give the most reasonable amount of fluid to move through air, to create an aerodynamics force.
Afterburner (reheat): The component in jet engines to add additional fuel for an aeroplane to take off smoothly.
Air bearing: A bearing which separates moving surfaces apart by a layer of air.
Air flow:
- Around the Bend: The study of observing air flow around a bend to measure the pressure distribution.
- Visualisation: The study of observing air moment to reduce the risk of a product or process.
Antoine Equation: A simple equation created by French engineer Louis Charles Antoine to describe the correlation between the vapour pressure and temperature of components.
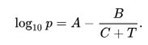
Angle of Incidence: in geometric optics, the angle of incidence is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal.

Arch:
- Fixed: A statically structured arch designed to hang different masses on a weight hanger.
- Three-pinned: A three-pinned arch structure designed to hold various loads to show the relationship between the masses and horizontal thrust produced from the arch structure.
- Two-pinned: A two-pinned arch structure designed to hold various loads to show the relationship between the masses and horizontal thrust produced from the arch structure.
Archimedes Principle: A fluid mechanics law which states that a body is totally or partially immersed in a fluid is subject to the weight of the fluid in an upward direction.
Aspect Ratio: The ratio between the height and width of the aerofoil.
Automatic Data Acquisition: Cost-effective and user-friendly data acquisition software used on TecQuipment’s products for over 60 years.